Product Description
Flange Rubber Gasket | Rubber Gasket | Gasket | Full face Gasket | Raise face Gasket | flange rubber gasket
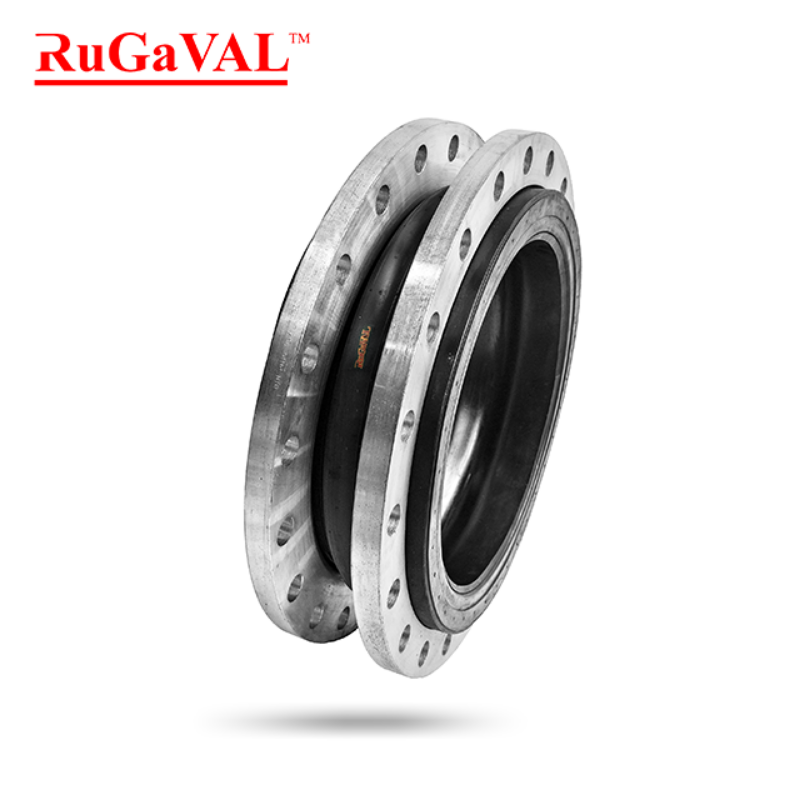
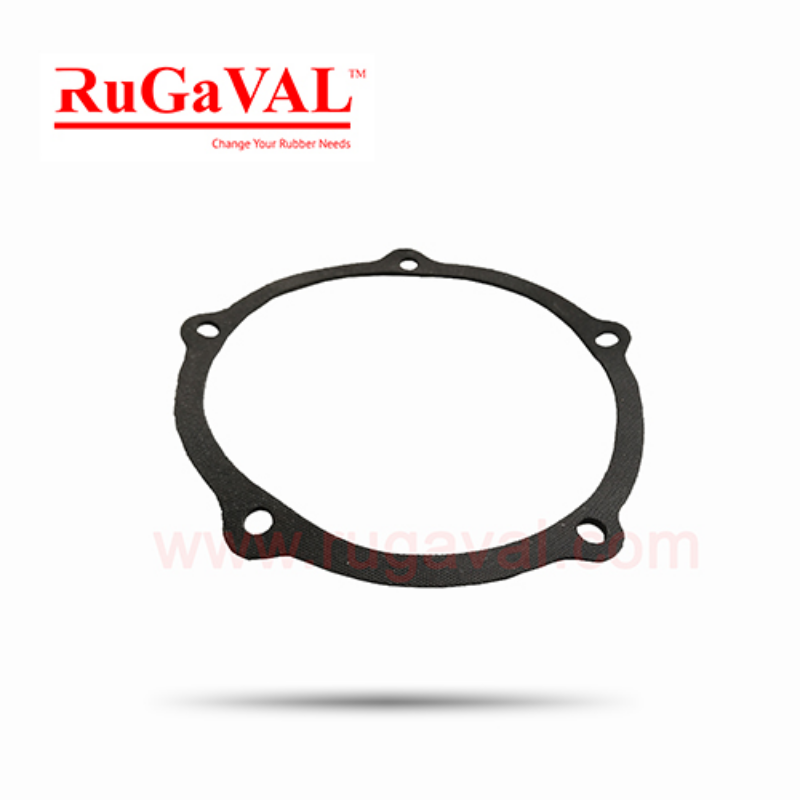
Flange Rubber Gasket
We manufacture and supply pipe gaskets, otherwise known as flange gaskets, in a range of materials. We hold dedicated tooling for the majority of standard sizes and tables and can manufacture special or one-offs to your own measurements and specifications. If you can’t find the information you’re looking for here, or wish to place an order then please contact us. The prices of pipe gaskets depend upon volume, material and thickness so please contact us for a quotation.
Different Types of Pipe Gaskets
The most commonly used gaskets in piping are standard flange gaskets in rubber. For particularly large pipes, gaskets can be manufactured in segments of rubber and joined together.
Standard Sizes and Dimensions
Pipe gaskets are made to fit the size of standard pipes or flanges. The most common standards are BS10 (British/Australian), PN/DIN (European), ASA/ANSI (USA) and JIS/KS (Japanese/Korean).
For ease of reference you can download some of the most common pipe gasket dimension charts here.
- Gasket Tables for PN Designated Flanges (DIN)
(To BS EN 1514-1:1967. PN 6, PN 10, PN 16, PN 25, PN 40)
- Gaskets for Class designated Flanges Suitable for ANSI Standard Flanges (ASA)
(To BS EN 12560-1:2001: ASME B16.21 Class 150, Class 300, Class 600; ASME B16.47 A Class 150, Class 300, Class 600; ASME B16.47 B Class 150, Class 300, Class 600)
- Gasket Tables for BS10 Flanges
(To BS 3063:1965: Table A, Table B, Table E, Table F, Table H, Table J, Table K)
Material Selection
Pipe gaskets can be manufactured from many different gasket materials. The right material to use depends upon the application and the environment in which the gasket will be used. The contents of the pipe, including the range of temperatures and pressures under which it is expected to operate will dictate material selection. Material specification should also take into account the flange being used. If you are in doubt about which material you need, please contact us for technical support.
For diesel or other fuels are nitrile rubber (BS 2751) should be used. Because of the extra additives in modern fuels, lower grade nitrile can be affected and break down. This is mistakenly blamed on the fuel itself when in reality it is caused by the corrosive nature of the additive.
If you are specifying for a particular chemical then please see our guide to gasket chemical resistance.
What is the Minimum/Maximum Thickness for Pipe Gaskets?
The thickness of a pipe gasket is governed by several requirements. The condition of the surface of the flange face has an important part to play. A thicker gasket may be required for a poor quality surface, as it will flow into and takes up the deformities on the face ensuring a good seal. With a clean and smooth flange face, a thinner gasket can be considered.
Pressure and media are other factors that can decide the thickness of gasket required. Putting too thick a gasket into a flange joint will increase the surface area that the system pressure can work against. For this reason, as a general rule: the thinner the gasket the better.
Common thicknesses of gasket material for pipe flanges are 1.5mm and 3mm.
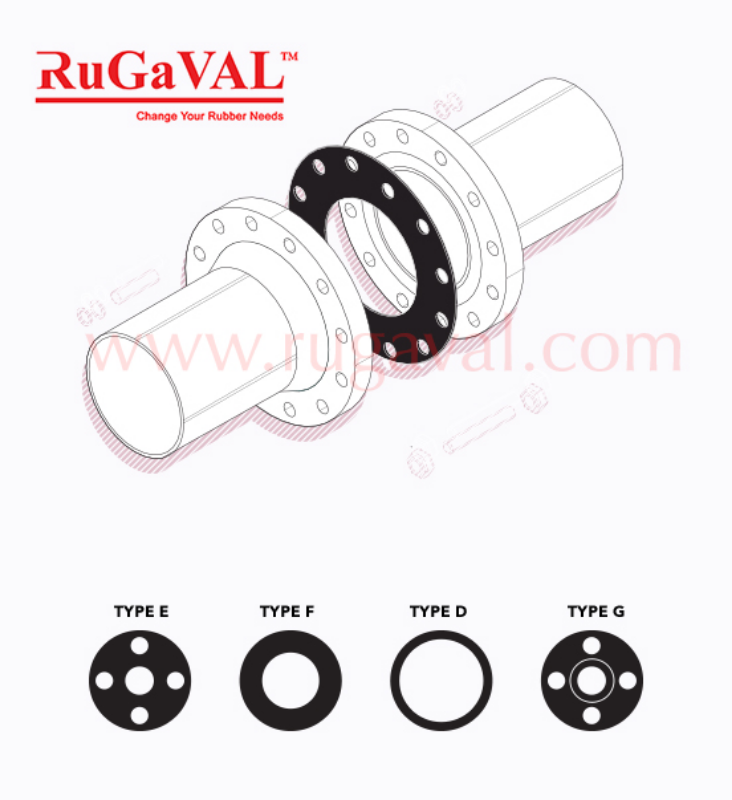
Full-Face or IBC Gaskets
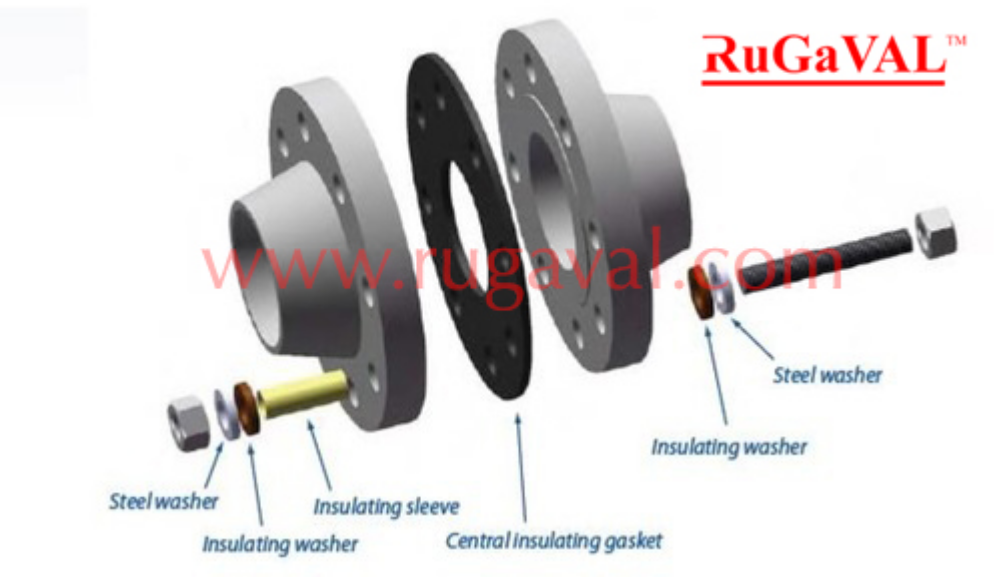
Pipe gaskets can be either full-faced or inner bolt circle (IBC). Full faced gaskets have bolt holes in them and cover a large part of the face of the flange. IBC gaskets, otherwise known as ring-type or raised-faced joints, sit inside the bolts fastening the pipe flanges.
How to Specify a Pipe Gasket
If you know the standard size of gasket you require then we will simply need to know: the material required; the thickness required; whether you need full-faced or IBC gaskets and the quantity.
If the part is a special, in addition to the above information we will also need to know: the outer diameter (O.D.), the inner diameter (I.D.), the pitch circle diameter (P.C.D.) and the number of holes.
We may also need to know: the operationg conditions (chemical resistance required, operating temperature, operating pressure and state of the flanges).
Flange Bolt Tightening Sequence
To obtain a leak-free flange connection a proper gasket installation is needed. The bolts must be given the correct bolt tension and the total bolt strength must be evenly divided over the whole flange face.
On the first pass lightly tighten the first bolt then the bolt directly across, or 180º from the first bolt. Move 90º round the pipe for the third bolt and then directly across for the fourth. Continue this sequence until all bolts are tightened.
Contact Details
Flange Rubber Gasket | Rubber Gasket | Gasket | Full face Gasket | Raise face Gasket | flange rubber gasket
| Supplier | : | Rugaval Rubber Sdn Bhd |
| : | rugavalrubber@gmail.com | |
| Phone | : | 60351918961 |
| Fax | : | 60351915961 |
| Location | : | Selangor, Malaysia |
Enquiry Box
Other Products




 Loading...Please Wait.
Loading...Please Wait.